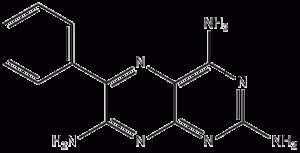
MecoBalamin ແມ່ນສໍາລັບການປິ່ນປົວຂອງຄວາມຜິດປົກກະຕິຂອງເສັ້ນປະສາດຂອງຜູ້ອໍານວຍການ
ລາຍລະອຽດຂອງຜະລິດຕະພັນ
| ຊື່ | MecoBalamin |
| ຫມາຍເລກ | 13422-55-4 |
| ສູດໂມເລກຸນ | C63H90CCO13O13O14P |
| ນ້ໍາຫນັກໂມເລກຸນ | 1343.4 |
| ຈຸດລະລາຍ | > 190 ° C (ທັນວາ.) |
| ການລະລາຍ | DMSO (ເລັກນ້ອຍ), methanol (sparingly), ນ້ໍາ (ເລັກນ້ອຍ) |
| ອັດຊາຍະ | 99% |
| ການເກັບຮັກສາ | ປະທັບຕາໃນແຫ້ງແລ້ງ, ເກັບຮັກສາໄວ້ໃນຕູ້ແຊ່ແຂງ, ພາຍໃຕ້ -20 ° C |
| ແບບຟອມ | ແຂງ |
| ສີ | ແດງສີແດງ |
| ການຫຸ້ມຫໍ່ | PE BAG BAG + ກະເປົາອະລູມິນຽມ |
ກຸນທະສັນ
MecoBalamin; MECOBALAMING; MethylcObalamin; cobylcoplamin;
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານການຢາ
ຫນ້າທີ່ Physiological
MethylcObalamin ແມ່ນຢາສໍາລັບການປິ່ນປົວຄວາມຜິດປົກກະຕິຂອງເສັ້ນປະສາດຂອງຜູ້ອໍານວຍການດ້ານອຸປະກອນ. ເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບການກະກຽມວິຕາມິນ B12 ອື່ນໆ, ມັນມີຄວາມສາມາດໃນການຂົນສົ່ງເນື້ອເຍື່ອເສັ້ນປະສາດ. ມັນສາມາດສົ່ງເສີມການເຜົາຜະຫລານ lip-lip-custe-lipid ໂດຍຜ່ານປະຕິກິລິຍາປ່ຽນ methyl ແລະສ້ອມແປງເນື້ອເຍື່ອເສັ້ນປະສາດທີ່ເສຍຫາຍ. ມັນມີບົດບາດຂອງ coenzyme ໃນຂະບວນການ Synthesizing methionine ຈາກ homocyine, ໂດຍສະເພາະແມ່ນການສັງເຄາະຂອງ nucleosis ຈາກ deoxyuridine, ແລະສົ່ງເສີມການສັງເຄາະຂອງ DNA ແລະ RNA. ນອກຈາກນັ້ນ, ໃນການທົດລອງຈຸລັງ glial, ຢາຈະເພີ່ມກິດຈະກໍາຂອງ Methionine Synthase ແລະສົ່ງເສີມການສັງເຄາະຂອງ myelin lipid lipid. ການປັບປຸງຄວາມຜິດປົກກະຕິກ່ຽວກັບທາດເຫຼັກສາມາດສົ່ງເສີມການສັງເຄາະທາດໂປຼຕີນຈາກທາດໂປຼຕີນຈາກກະດູກໃກ້ກັບປົກກະຕິ, ແລະຮັກສາຫນ້າທີ່ຂອງເພົາ. ການສີດຢາ Methylcobalmin ຍັງສາມາດຍັບຍັ້ງການປະຕິບັດຄວາມວຸ້ນວາຍທີ່ຜິດປົກກະຕິຂອງເນື້ອເຍື່ອປະສາດ, ສົ່ງເສີມການເຕີບໂຕເຕັມເສັ້ນທາງແລະການແບ່ງປັນຂອງ Erythroblasts, ແລະປັບປຸງໂລກເລືອດຈາງ. MethylcObalamin ສາມາດຟື້ນຟູຈໍານວນເມັດເລືອດແດງ, hemoglobin, ແລະ hematocrit ຄຸນຄ່າຂອງຫນູທີ່ຖືກຫຼຸດລົງຍ້ອນການຂາດ B12. ນໍາໃຊ້ກັບໂຣກເຍື່ອຫຸ້ມສະຫມອງອັກເສບແລະເສັ້ນປະສາດທີ່ເກີດຈາກການຂາດວິຕາມິນ B12.
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານການຢາ
MethylcObalamin ແມ່ນອະນຸພັນຂອງວິຕາມິນ B12. ມັນຖືກຕັ້ງຊື່ຕາມໂຄງສ້າງທາງເຄມີຂອງມັນ. ມັນຄວນຈະຖືກເອີ້ນວ່າ "methyl vitamin b12". ມັນສາມາດສົ່ງເສີມການເຜົາຜານໄຂມັນຂອງໄຂມັນ, ກະຕຸ້ນການສັງເຄາະຂອງ lecithin ໃນຈຸລັງ schwann, ສ້ອມແປງກາບ myelin, ແລະປັບປຸງຄວາມໄວຂອງເສັ້ນປະສາດ; ມັນສາມາດເຂົ້າໄປໃນຈຸລັງເສັ້ນປະສາດໂດຍກົງແລະກະຕຸ້ນການສືບພັນຂອງແກນທີ່ເສຍຫາຍ; ກະຕຸ້ນການສັງເຄາະທາດໂປຼຕີນຂອງຈຸລັງເສັ້ນປະສາດ, ສ້າງຄວາມເຂັ້ມແຂງໃຫ້ແກ່ Axon Anabolism, ປ້ອງກັນ Axon Degeneration; ເຂົ້າຮ່ວມໃນການສັງເຄາະອາຊິດນິວເຄຼຍ, ສົ່ງເສີມການເຮັດວຽກ hemematopoetic. ຄລີນິກ, ມັນມັກຈະຖືກນໍາໃຊ້ໃນການຮັກສາໂລກເບົາຫວານ Neuropathy, ແລະການນໍາໃຊ້ໄລຍະຍາວຂອງມັນກໍ່ມີຜົນກະທົບທີ່ແນ່ນອນກ່ຽວກັບອາການແຊກຊ້ອນຂອງເສັ້ນເລືອດໃຫຍ່ໃນໂລກເບົາຫວານ. Methylcobalamin ສ່ວນໃຫຍ່ແມ່ນໃຊ້ສໍາລັບພະຍາດເຍື້ອທາງດ້ານປະເທດທີ່ເກີດຈາກໂຣກເບົາຫວານແລະໂຣກເລືອດຈາງທີ່ເກີດຈາກການຂາດວິຕາມິນ B12. ມັນຖືກນໍາໃຊ້ຢ່າງກວ້າງຂວາງດ້ານຄລີນິກທີ່ມີຜົນຂ້າງຄຽງທີ່ມີຫນ້ອຍ.
ການນໍາໃຊ້
ມັນຖືກນໍາໃຊ້ເພື່ອຮັກສາພະຍາດຂອງລະບົບປະສາດ, ບັນເທົາອາການເຈັບແລະບັນເທົາອາການເຈັບປວດຢ່າງໄວວາ, ປັບປຸງຄວາມເຈັບປວດທີ່ເກີດຈາກຄວາມເສີຍເມີຍ